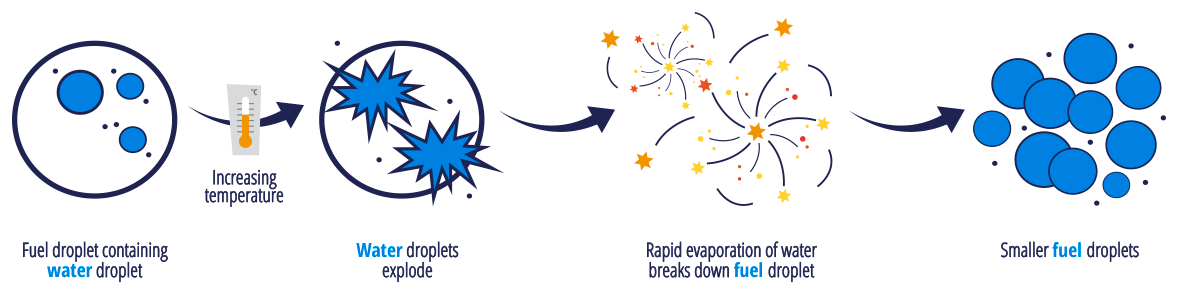
The technology is scientifically based on the emulsion of two or more immiscible liquids. In this case, water is blended with a conventional fuel and the resulting product can be used as a fuel source.
Emulsification of oils
Oil emulsification
New advances in technology have recently made emulsions fuels much more stable and reliable – they now serve as a viable substitute to traditional petroleum-based fuels.
Using advanced nanotechnology developed by Novus Oil in cooperation with TalTech, our system is able to keep the emulsion stable for up to 12 months, depending on the storage conditions.
Oil emulsification products

EMULSION DIESEL
Diesel oil emulsions are direct substitutes for diesel in all diesel applications, including compression ignition engines (high-, medium- and low-speed diesel engines), combustion turbines, furnaces and boilers. Depending on its application, the water content of emulsion diesel can vary between 5% and 30% by volume; however, the standard product contains around 10% water and less than 2% additive, with the balance comprising diesel.
Emulsion diesel’s unique combustion characteristics result in significant environmental benefits over ordinary diesel. The common ranges of emulsion diesel reductions are:
EMULSION HEAVY FUEL OIL
HFO emulsions are direct substitutes for HFO, which is sometimes called fuel oil, bunker or residual oil. The water content of HFO can vary between 10% and 30% depending on the application and the customer’s needs. Fuel oil emulsions (FOE) are designed for boiler applications and large, slow–speed internal combustion engines. FOE can be used in utility, industrial and commercial boilers, as well as marine engines.
Water content ranges between 10% and 30%, while additive content ranges between 0.05% and 2.0%. FOE fuel can be tailored to enhance various boiler operating conditions. Fuel tailoring is mainly achieved by varying the water content.
The benefits of emulsion heavy fuel oil are related to the environment. More complete carbon burnup reduces the opacity (smoke) and particulate matter emanating from the stack. In addition, secondary atomisation allows boilers to operate with less excess O2, which consequently reduces NOx emissions. NOx is created when nitrogen (N2) is combined with oxygen in the presence of heat. Reduced oxygen requirements translate directly into lower NOx emissions.
Low NOx water in oil emulsion fuels
Fuels from recycled oils
Fuel Oils
Bunker fuels (ISO 8217:2010)
Advantages of use of emulsified oils
Advantages are seen in all applications, including secondary atomisation, lower fuel use and significantly fewer emissions of greenhouse gases. More particularly:
ENGINES
The advantages of using emulsion fuels in internal combustion engines are:
BOILERS
In addition to the same advantages as engines:
Real life savings from emulsification Technologies by BBS
Electricity production (liquid fuel IC engine):
Heat generation (liquid fuel boilers):
Shipping (IFO, RMG, MGO, MDO and Diesel):
Road transport (Diesel):
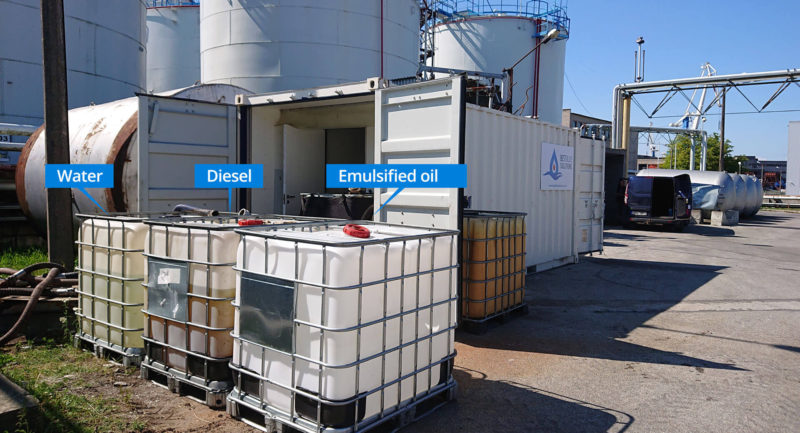

Background to emulsions
Oil emulsification customers




